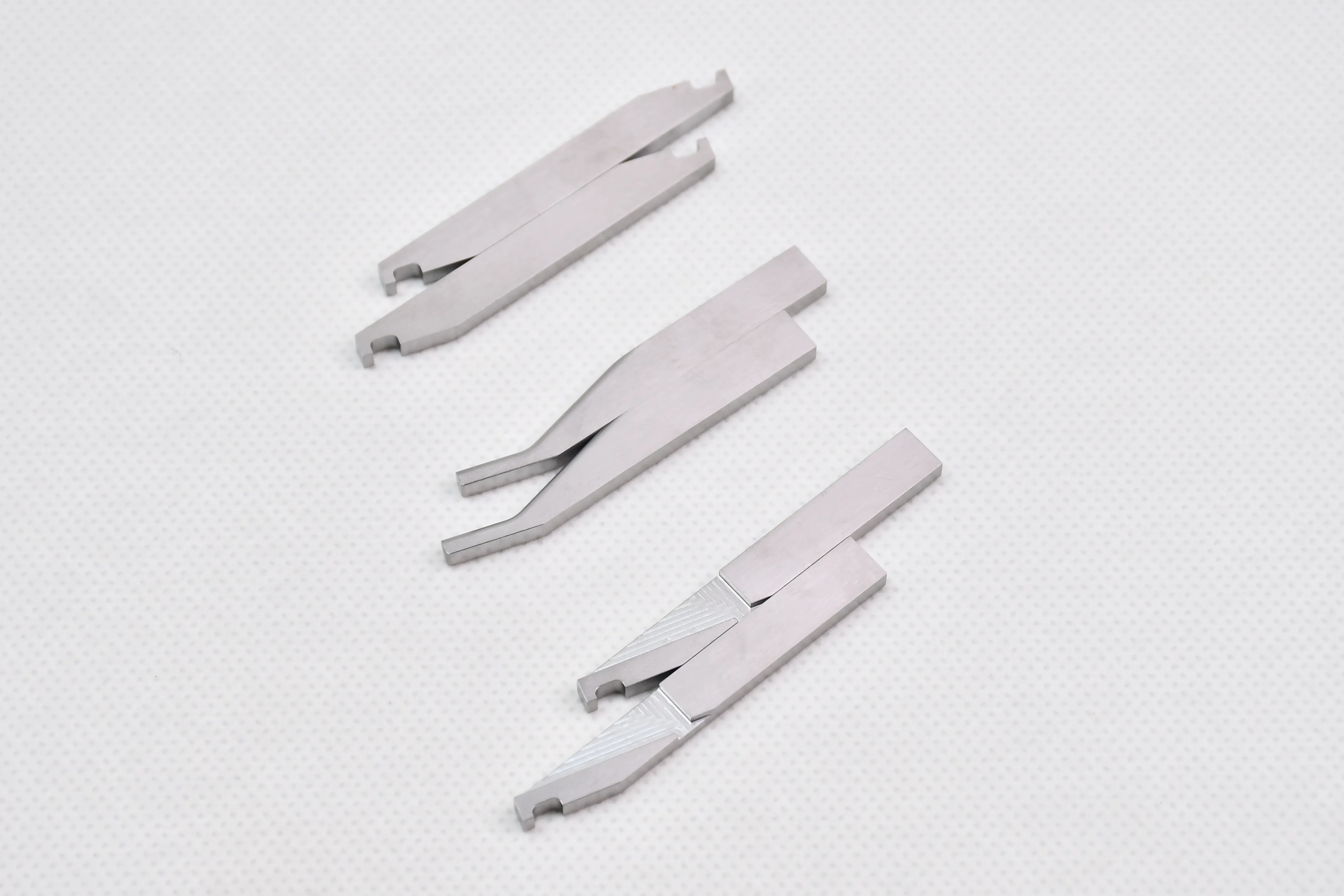
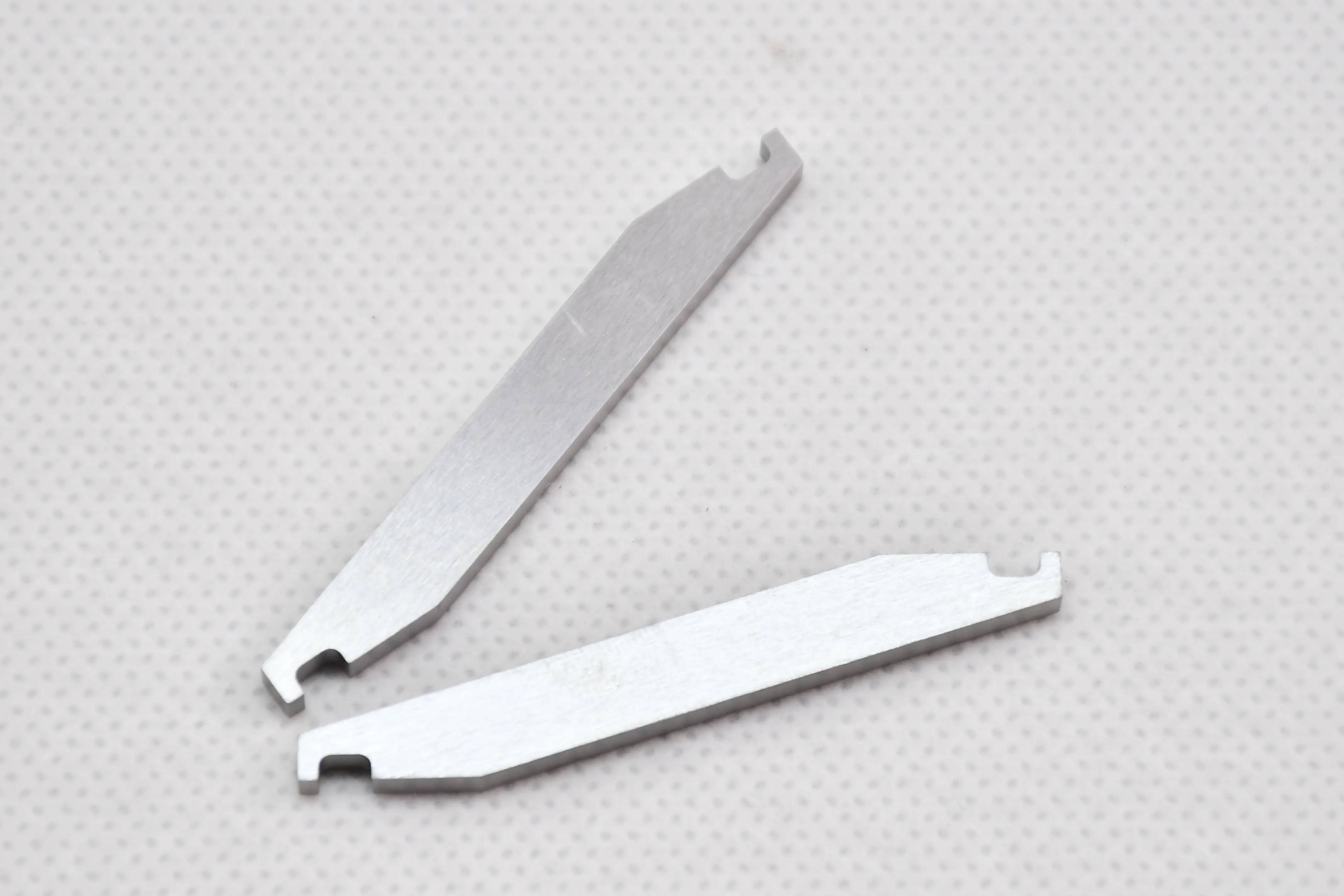
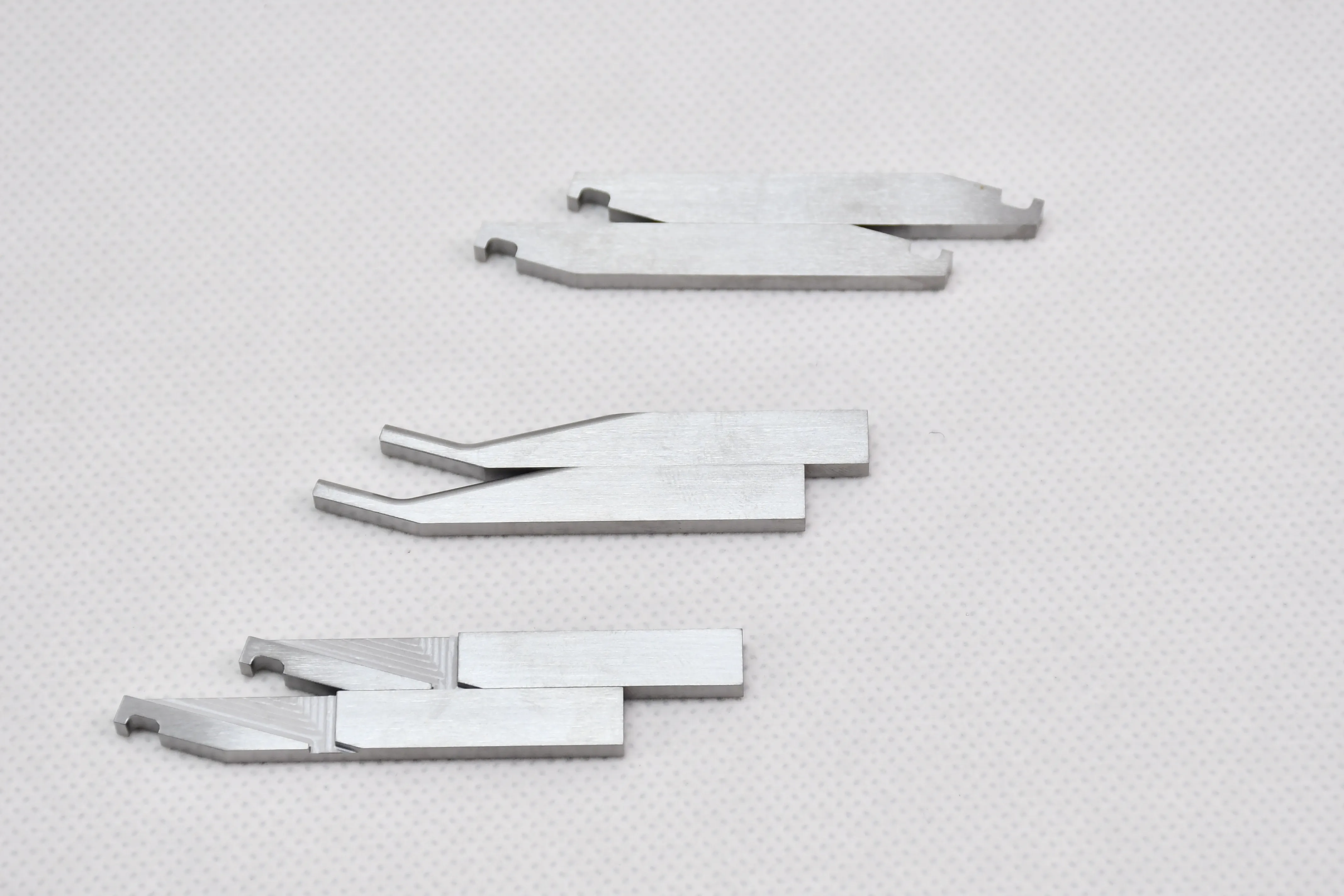
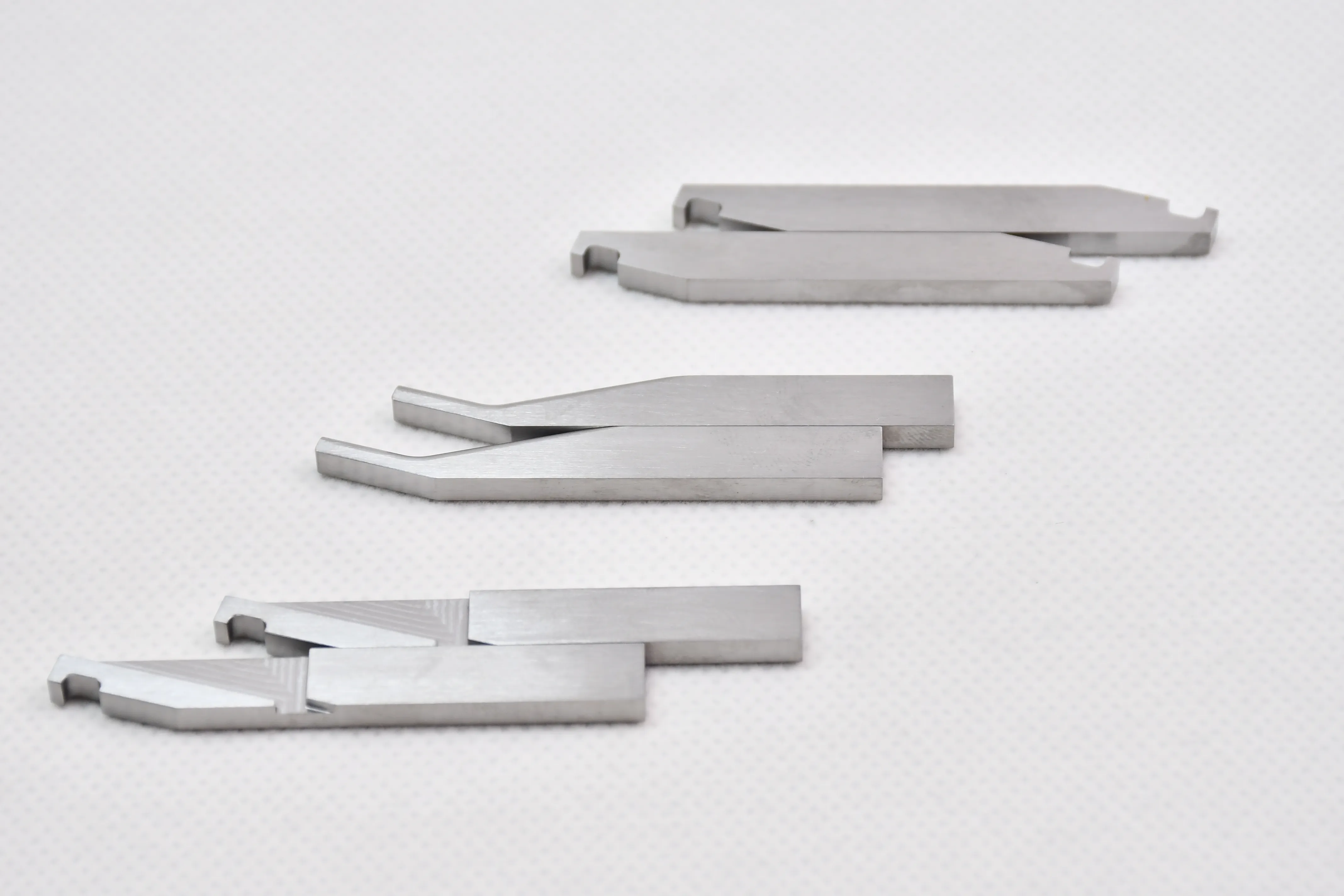
Tungsten-copper electrodes
| Payment Type: | T/T |
| Incoterm: | FOB,CIF,EXW,FCA,Express Delivery |
| Min. Order: | 50PCS |
| Transportation: | Ocean,Air,Express |
Attributes
Model No.: JDTG-TC-103
Brand: ZZJD
Place Of Origin: China
Size: Support customiztion
Material: Tungsten
Lead Time: 30 days
PACKAGING & DELIVERY
Selling Units : PCS
Package Type : Standard export packing
DESCRIPTION
Tungsten-copper (W-Cu) electrodes are composite materials made by powder metallurgy, combining the high melting point, excellent electrical conductivity, and arc resistance of tungsten with the high thermal conductivity and good machinability of copper. They are widely used in high-temperature, high-current electrical discharge scenarios where pure metals fail to meet performance requirements.
Core Properties of Tungsten-Copper Electrodes
Tungsten and copper are immiscible (do not form alloys at the atomic level), so the composite retains the advantages of both components:
|
Property |
Tungsten Contribution |
Copper Contribution |
Key Benefit |
|
Electrical Conductivity |
High electron mobility |
Excellent conductivity |
Low energy loss during current transmission |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
Heat resistance |
Rapid heat dissipation |
Prevents electrode melting/burning in high-temperature arcs |
|
Arc Resistance |
High melting point (3422°C) |
No evaporation at arc temperatures |
Resists erosion and deformation under arc impact |
|
Machinability |
— |
Good ductility and machinability |
Easy to process into complex shapes (holes, grooves) |
|
Density |
High density (19.3 g/cm³) |
Moderate density (8.96 g/cm³) |
Adjustable density (10–18 g/cm³) via tungsten content |
Common tungsten content ratios: 70%W-30%Cu, 80%W-20%Cu, 90%W-10%Cu — higher tungsten content improves arc resistance, while higher copper content enhances thermal conductivity.
Key Applications
1. Tungsten-copper electrodes are irreplaceable in high-energy electrical equipment due to their unique performance:
2. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Used as EDM electrodes for processing hard metals (e.g., tungsten steel, titanium alloys) and precision molds. The high thermal conductivity of copper quickly dissipates heat from the discharge area, avoiding electrode burnout.
3. Welding Electrodes: Applied in resistance welding (e.g., spot welding of thin metal sheets) and plasma arc welding. They resist arc erosion and maintain stable current transmission.
4. High-Voltage Switchgear: Used as contact electrodes in circuit breakers, load switches, and lightning arresters. They withstand arc impact during switching and have low contact resistance.
5. Aerospace & Military: Used in rocket engine ignition electrodes, radar microwave components, and nuclear reactor thermal conductivity parts, adapting to extreme environments of high temperature and high pressure.
Advantages Over Pure Tungsten or Copper Electrodes
|
Material |
Limitation |
Tungsten-Copper Composite Advantage |
|
Pure Tungsten |
Poor machinability, low thermal conductivity |
Good machinability + rapid heat dissipation |
|
Pure Copper |
Low melting point, easy to burn in arcs |
High arc resistance + no deformation under high temperature |


 EN
EN AR
AR FR
FR DE
DE HI
HI IT
IT JA
JA KO
KO PT
PT RU
RU ES
ES ID
ID LV
LV VI
VI HU
HU MS
MS GA
GA BE
BE YI
YI EU
EU